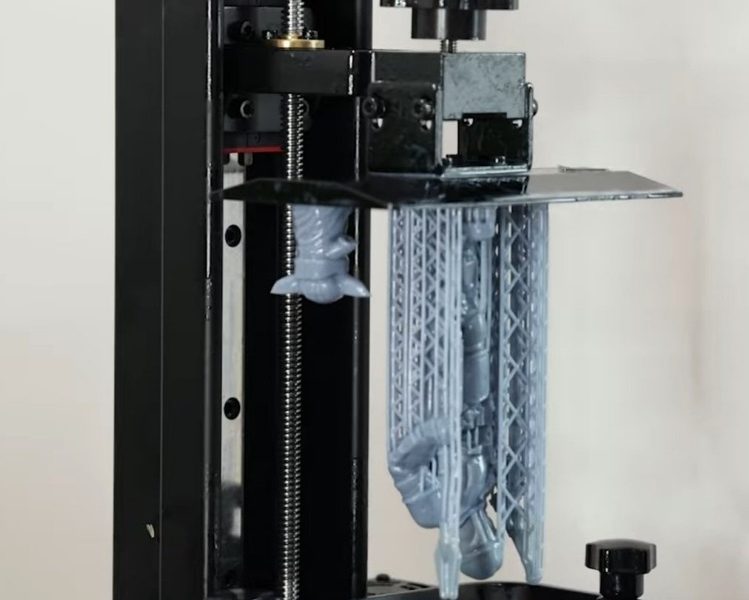
What is 3D Printing & How Does 3D Printing Work?
Special software “slices” the 3D model into thin horizontal layers that are stacked on top of each other. The model is then converted into a set of instructions that guide the 3D printer on how to create each layer.
Determine which materials you’ll work with and the specific services you’ll offer, including prototyping, production, custom items, and more. With Binder Jetting, an adhesive liquid binding agent is dispensed into a thin layer of powder material to build the metal part layer by layer. Unlike SLM and DMLS, no support structures are required for the Binder Jetting printing process. The layers bind together to form a solid object that is initially in a ‘green state’ also known as a ‘green part’.
A form of Powder Bed Fusion, SLS fuses small particles of powder together by use of a high-power laser to create a three-dimensional shape. The laser scans each layer on a powder bed and selectively fuses them, then lowering the powder bed by one thickness and repeating the process through completion. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic overwhelmed hospitals and increased the need for personal protective equipment. Many healthcare facilities turned to 3D printing to supply their staff with much-needed protective equipment, as well as the parts to fix their ventilators. Large corporations, startups and even high school students with 3D printers stepped up to the plate and answered the call. 3D printing will not only change how we make PPE and medical equipment, but also streamline prosthetics and implants.
Accept that your prints won’t be perfect
Step Five – Removal
Removing the finished parts from the printer will vary for different 3D printing technologies. In some case, like for Desktop machines, it is as simple as separating the print from the build platform. For some industrial 3D printers, the removal of a part is a technical process that requires professional skills and specialized equipment within a controlled environment. After you have a model to 3D print, you need to prep the file so the 3D printer can interpret the data and print your object. A slicer takes your 3D model’s file (which is typically an STL, M3F or OBJ file) and cuts the object into thin horizontal layers that the 3D printer’s print head follows layer-by-layer. The most popular slicing software among consumer and light industrial grade printers is Simplify3D.
And yeah, their robot AI developed a new chemical that acts as a catalyst that produces oxygen. It did a bunch of modelling simulations, it did a bunch of experiments, the kind of thing that a real, human chemist could do, but it would take a long time. And the lead investigator on that project says, you know, we can scale this up, we can produce loads of oxygen.
What do you need to 3D print?
The team are already looking at this as they progress this research, and Robert is optimistic that this technique, even beyond robots, could help make medical implants… The one major downside of ultrasonic additive manufacturing printers is they need cutting machines to separate and finish the model. Similar to SLA, DLP printers (such as those made by Wanhao and SparkMaker) cure multiple layers at once using a digital light projector. This results in faster print times but may sacrifice some resolution compared to SLA. A large part of the 3D printers we have is not based on filament but on powder. Laser sintering, Multi Jet Fusion and Metal 3D Printing is used to create 3D prints in materials such as polyamide, alumide, titanium, and rubber-like. Your 3D printer will then interpret the instructions, layer by layer, as it lays down plastic or other composite materials.
Progress in materials science and the lapse of numerous patents increased the affordability of 3D printing. Another form of Powder Bed Fusion, MJF uses a sweeping arm to deposit powder and an inkjet-equipped arm to apply binder selectively on top. Next, a detailing agent is applied around the detailing agent for precision. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) also utilizes this same process but with metal powder specifically. CLIP is amongst the faster processes that use Vat Photopolymerisation. The CLIP process utilizes Digital Light Synthesis technology to project a sequence of UV images across a cross-section of a 3D printed part, resulting in a precisely controlled curing process. Read more about impression 3d Strasbourg here. The part is then baked in a thermal bath or oven, causing several chemical reactions that allow the part to harden.
Why Are 3D Printers Important to the Future?
The build begins with a scanning recoater laying down a uniform, thin layer of metal powder across the working area. The recoater is refilled from supply bins of metal powder located at each end of the scan. One reason why this is a great technology is that no supporting structure is needed.
Within each type of process there are unique technologies, and for every unique technology there are also many different brands selling similar printers. The major limitation of subtractive manufacturing is that the cutting tool must be able to reach all surfaces to remove material, which limits design complexity quite a lot.
Accuracy is therefore the measure of a printed part’s closeness to the digital version, and this measure is usually expressed as a percentage or in millimeters, e.g. ± 1% or ± 0.5 mm. The speed of 3D printers varies; according to all3dp.com, slower printers work at around 40 to 50mm/s, while the fastest print at around 150mm/s. You can typically set the 3D printing speed of your printer in the settings of your 3D printing software. Here at 3DPrint.com we are always seeking to educate the general public about the incredible technology known as 3D printing. Therefore we have set out to create a brief, yet informative guide on 3D printing, how it works, and the various technologies involved.